In 2018, the European Union implemented a series of data protection reforms known as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). In essence, GDPR replaced all the different data protection laws with a single set of rules that applies to every EU state. Many businesses had to change their policies to be GDPR compliant, however, despite the transition period, there’s still a lot of confusion regarding the new rules.
So what is GDPR and how can you make your business compliant?
In this article, you’ll learn how to be GDPR compliant without having to read the dry EU data protection directive. We’ll help you understand what GDPR is and tell you what steps you need to take to make your site GDPR compliant.
What Is GDPR?
GDPR is a data protection directive in the European Union designed to protect the online privacy of EU citizens. It regulates the way personal data is used and what type of data websites can collect about you. Despite being an EU regulation, GDPR applies to all websites accessed by users from the EU. As a result, websites and businesses have to be GDPR compliant or block EU traffic.
With that in mind, here are the key aspects of GDPR that might affect your business:
- Your site has to clearly inform the visitors that their personal data is being collected.
- You also need to disclose how and why their data is collected and stored.
- If users ask you to delete personal data you collected, you must comply with the request in most cases.
- Users can also request a copy of all the personal information you store.
- If one of your business’s main activities is to gather and store personal data, you need to hire a data protection officer.
- If your website is breached and the personal information of your users leaks out, you have 72 hours to report the breach.
- Breaking the GDPR regulation can lead to fines of up to €20 million (~$24 million) or 4% of your company’s annual turnover.
The main purpose of GDPR is to protect people and their personal information from data breaches. Now the question is, what types of data fall under GDPR?
Types of Data Regulated by GDPR
Whether you built your website from scratch or used a WordPress theme, your site gathers different types of data. Websites collect information in different ways, including through analytics, WordPress forms, subscription forms, contact forms, and email marketing campaigns.
In short, all personal data falls under GDPR, but we can break it down into the following types:
- Genetic and health information.
- Biometric data.
- Political and/or religious views.
- Race, ethnicity, and gender.
- Web data such as your IP address and cookie data
As long as your business stores any of the aforementioned data of EU citizens, your site needs to be GDPR compliant. Remember that this applies even if you don’t have a presence within the European Union’s borders.
Steps Required To be GDPR Compliant
When you read about your responsibilities as a website owner you might feel overwhelmed and decide it’s easier to block all incoming EU traffic. Don’t let GDPR discourage you. Below are the main steps you need to take to be GDPR compliant.
1. Improve Your Privacy Policy
Be transparent with collecting, storing, and sharing data. Your website should contain a detailed privacy policy that clearly explains data collection practices, data protection, the usage of cookies, and data sharing. A good privacy policy should at least include the following points:
- You don’t sell your users’ private data.
- You don’t share private data unless the law obligates you.
- The types of data you collect.
- The reasons why you collect data and how you use it.
- How you protect user data.
- How your plugins collect and use data.
Be as clear as possible by using simple language that doesn’t leave any room for interpretation and you’ll have a clear-cut transparent privacy policy.
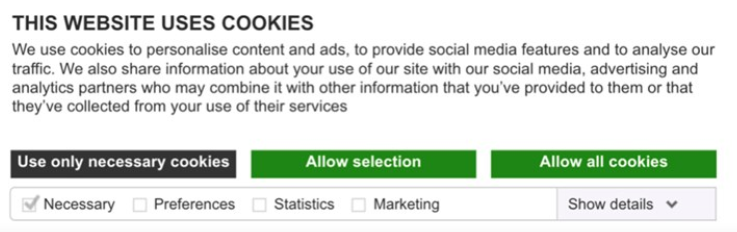
2. Create a Cookie Collection Notice
According to the GDPR, cookies count as personal data, so you need to ask your users for consent before using cookie data. Place an explicit cookie collection notice on your website and make sure you allow users access to your website even if they don’t give consent. Your users should also have an easy way of withdrawing their consent at any time.
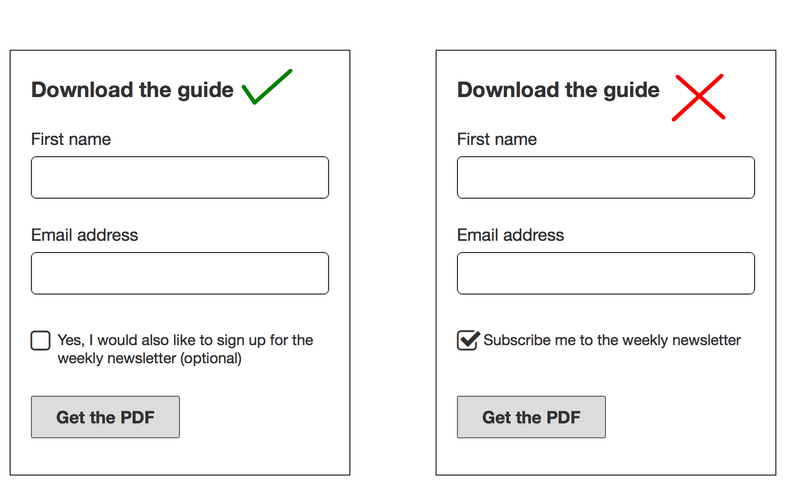
3. Display Notices On All Website Forms
It’s standard practice to collect some user data through various types of submission forms. If you want to continue collecting email addresses and other details, post a data collection notice. Don’t gather any data before that point and without the user’s acknowledgment. Otherwise, your business could receive a hefty fine for breaking GDPR.
Be as clear as possible with your wording and offer all the important details about collecting data. You should also avoid using pre-checked tick boxes. The user needs to understand that data collection is optional and that it requires their consent.
4. Make Sure All Plugins Are GDPR Compliant
If you’re using third-party plugins that collect data, like Google Analytics, you need to make the data anonymous. This can be challenging to do manually, but you can find GDPR-compliant plugins that handle this process for you. Just search for a tool with GDPR compliance settings.
5. Use the Double Opt-in
GDPR doesn’t make double opt-ins obligatory, but it’s highly recommended to use them. A double opt-in means you’re asking the user twice to acknowledge that they’re giving consent for data collection. This is particularly important for email list subscriptions.
To add a double opt-in, you need to first request consent through the website’s subscription form. Then the user should consent a second time by clicking a link they receive through email.
Using the double opt-in shows that you’re dedicated to data protection and privacy, and it also gives the authorities further proof that your site is GDPR-compliant.
6. Add Unsubscribe Links
Include easy-to-read unsubscribe links with every communication you send to your subscribers. Unsubscribing from your mailing list should be an easy process and instant.
7. Delete Personal Data on Request
GDPR gives users the right to be forgotten. This means they can request at all times for their data to be deleted. Always do as requested. This includes removing your users from mailing lists, deleting their accounts, and wiping any personal information you have about them. Even blog posts and forum comments count as personal data and should be removed if requested.
8. Don’t Buy Mailing Lists
Buying mailing lists isn’t recommended because you might be in violation of GDPR. In most cases, you can’t be sure whether those email addresses were collected with the users’ consent.
That said if you’re still determined to buy a mailing list, make sure you at least include unsubscribe links with every email you send.
Being GDPR Compliant Is Worth It
Open your website and business to EU citizens by following all the steps above. Being GDPR compliant might sound challenging at first, but it’s not that hard. It mostly involves being transparent about collecting data and asking for consent. As a bonus, non-EU users will see that your business cares about privacy and data protection and they’ll be more likely to trust you.